If you have any question, please contact us
If you have any question, please contact us
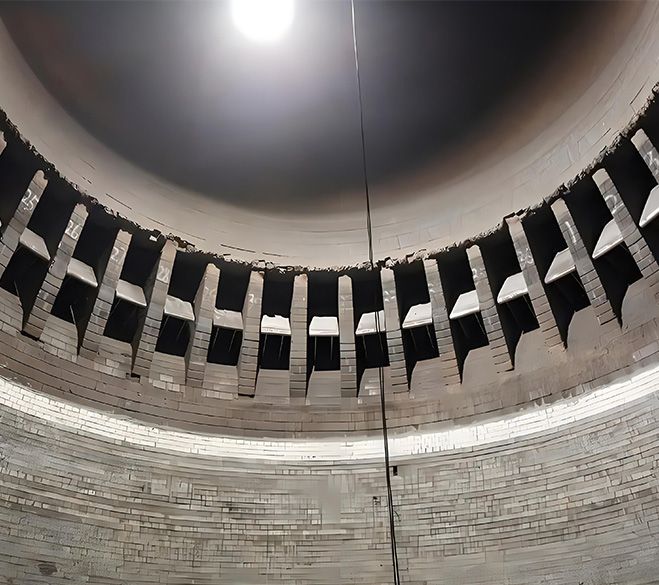




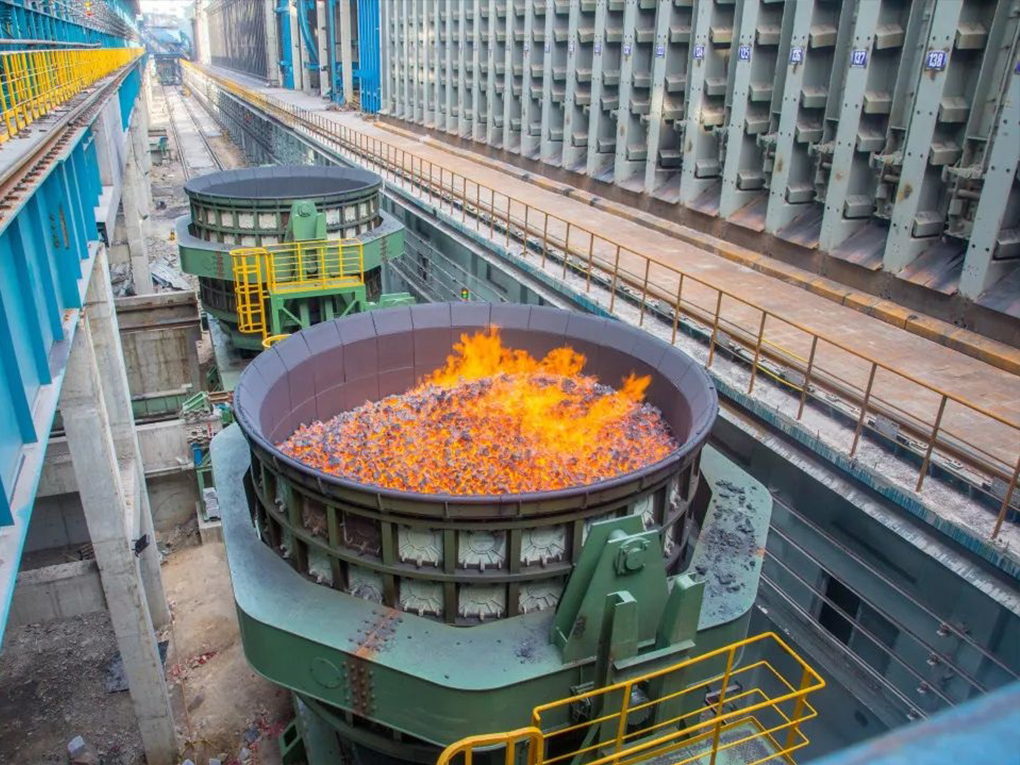
Dry quenching coke oven is a cooling device different from coke oven. Red coke is loaded from the top of the dry quenching oven, and low-temperature inert gases (e.g., nitrogen) are drummed by the circulating fan into the red coke layer of the dry quenching oven’s cooling chamber to absorb the red coke’s heat, and this process reduces the coke’s temperature to less than 180°C.
Dry quenching coke oven is a cooling device different from coke oven. Red coke is loaded from the top of the dry quenching oven, and low-temperature inert gases (e.g., nitrogen) are drummed by the circulating fan into the red coke layer of the dry quenching oven's cooling chamber to absorb the red coke's heat, and this process reduces the coke's temperature to less than 180°C. The dry quenching oven is designed to cool the coke in the dry quenching chamber by using an inert gas. The cooled coke is discharged from the bottom of the dry quenching oven, while the high temperature inert gas from the ring flue of the dry quenching oven flows through the dry quenching boiler, where it exchanges heat with water to produce steam, which can be used to generate electricity or drive other industrial equipment.

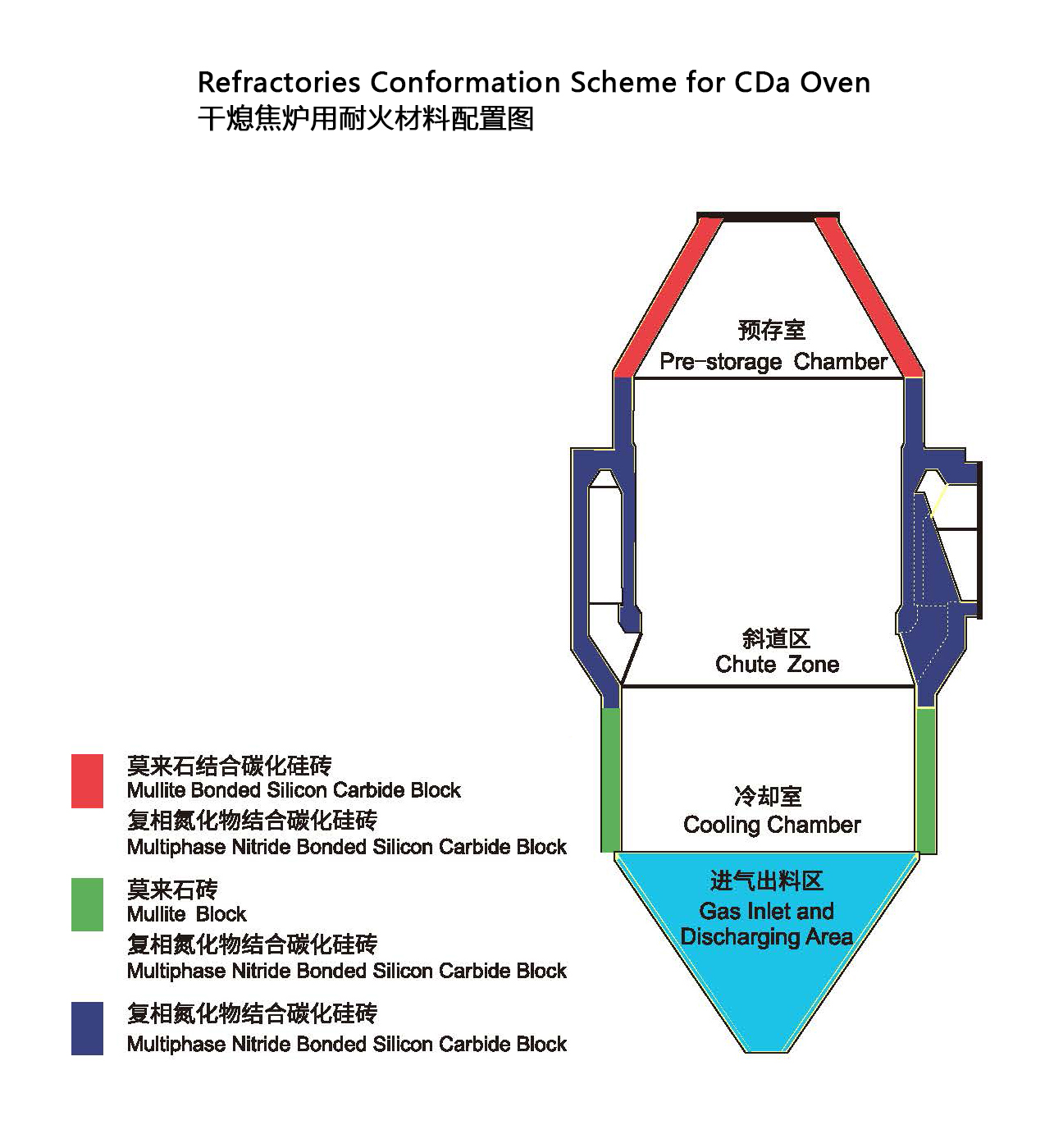
According to different application area, the refractory materials as follows:
1、Furnace mouth: mullite silicon carbide bricks
2、Pre-storage room: clay bricks, mullite bricks
3、Ramp: mullite silicon carbide bricks, mullite bricks
4、Ring duct: mullite bricks, clay bricks
5、Cooling room: mullite bricks, clay bricks, wear-resistant castable
6、Others: wear-resistant castable, lightweight insulation castable

| Refractory Datasheet for Dry Quenching | ||||||
| Item | Clay brick | Mullite Brick AM | Mullite brick BM | Mullite-Silicon Carbide Brick AT | Mullite-Silicon Carbide Brick BT | Silicon nitride bonded silicon carbide brick |
| SiC;% | / | / | / | ≥35 | ≥30 | ≥72 |
| Fe2O3;% | ≤1.6 | ≤1.3 | ≤1.3 | ≤1.2 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.7 |
| Al2O3;% | ≥40 | ≥55 | ≥55 | ≥30 | ≥40 | / |
| Refractoriness;℃ | ≥1690 | ≥1770 | ≥1770 | ≥1770 | ≥1770 | ≥1790 |
| Apparent porosity;;% | ≤22 | ≤18 | ≤17 | ≤17 | ≤21 | ≤17 |
| Bulk density;g/cm3 | ≥2.15 | ≥2.40 | ≥2.45 | ≥2.45 | ≥2.50 | ≥2.65 |
| Cold crushing strength;Mpa | ≥30 | ≥65 | ≥75 | ≥85 | ≥75 | ≥150 |
| 0.2MPa refractoriness-under-load/℃ | ≥1350 | ≥1500 | ≥1500 | ≥1500 | ≥1600 | / |
| Permanent Linear Change On Reheating;% (1350℃×2h) |
+0.1~-0.5 | +0.2~-0.3 | +0.2~-0.3 | +0.2~-0.3 | +0.2~-0.3 | / |
| Thermal shock stability (1100°C water-cooled);bout |
≥8 | ≥20 | ≥15 | ≥22 | ≥30 | ≥50 |
| Abrasion resistance | Good | Good | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Application | Loading area and non-working layer | Reserved segment cooling section circulation device |
Reserved segment cooling section circulation device |
Ramp area Furnace mouth part |
Ramp area Furnace mouth part |
Ramp area |